History
History
The Sustainable Development Goals Fund (SDG Fund) is the first development cooperation mechanism created to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
With an initial contribution from the government of Spain, the SDG Fund was created in 2014 in order to support sustainable development activities through integrated and multidimensional joint programmes. The SDG Fund has acted as a bridge in the transition from MDGs to SDGs, providing concrete experiences on how to achieve the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development and the SDGs.
The MDG Achievement Fund
For the design of its joint programmes, the SDG Fund builds on the experience, knowledge, lessons learned and best practices of the Millennium Development Goals Achievement Fund. Established in 2007 through an agreement between the Government of Spain and UNDP, on behalf of the UN system, the MDG-F operated in 50 countries. It worked through more than 27 UN agencies in collaboration with citizens, civil society organizations, and local, regional, and national governments to target vulnerable groups and tackle multidimensional development challenges.
The MDG-F was one of the largest and most comprehensive development cooperation mechanisms devised to support MDG attainment.
With a total contribution of approximately USD $900 million, the MDG-F financed 130 joint programmes in 50 countries around the world, in 8 areas: Children, Food Security and Nutrition; Gender Equality and Women’s Empowerment; Environment and Climate Change; Youth, Employment and Migration; Democratic Economic Governance; Development and the Private Sector; Conflict Prevention and Peace-Building; and Culture and Development.
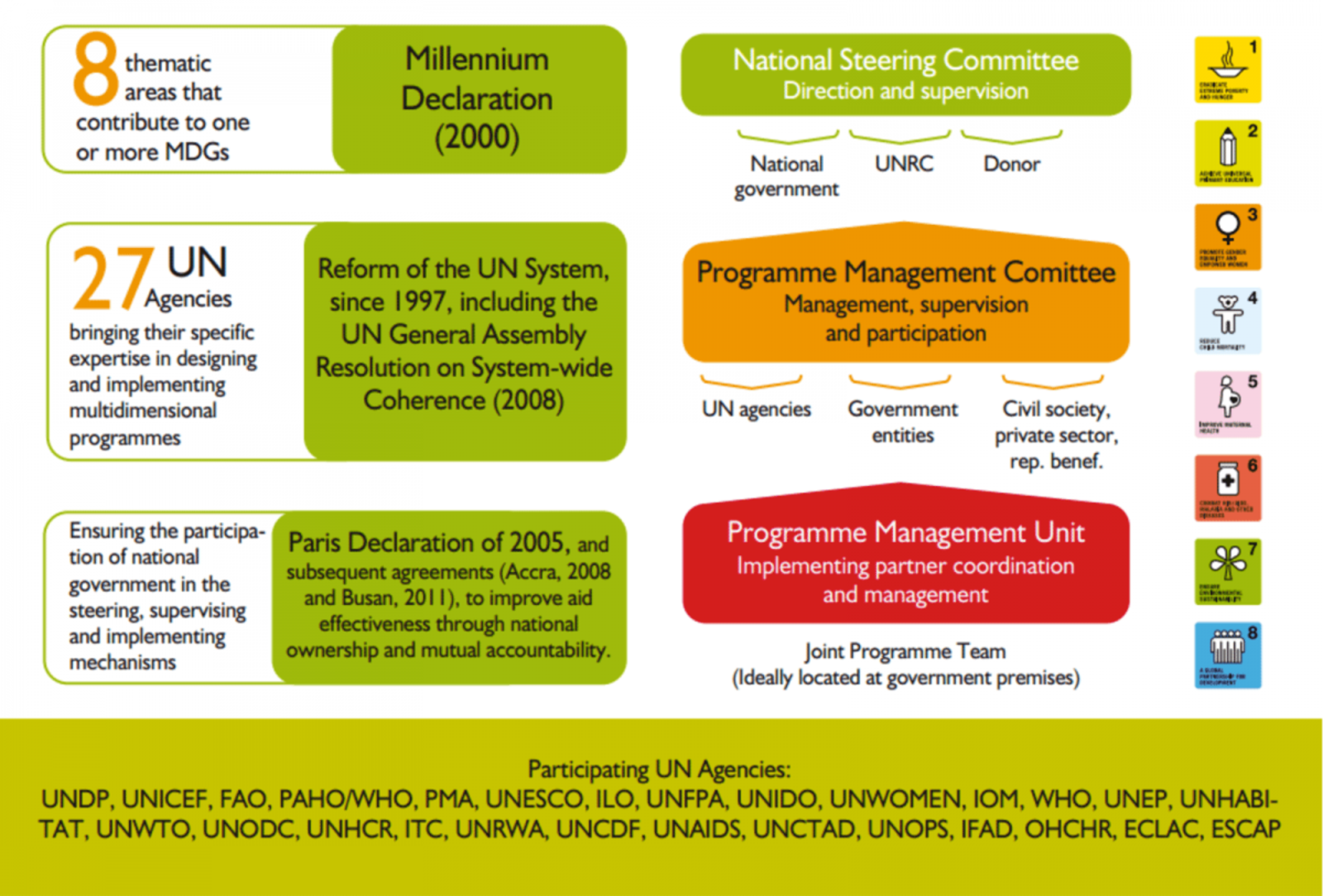
Figure 1. The MDG Achievement Fund´s approach
Learning from the MDGs
The MDG-F produced valuable insights on development cooperation. All this knowledge has been compiled in our library and is now accessible online. The SDG-F is disemminating and sharing the knowledge generated with development aid practitioners and decision-makers. The MDG-F country and global evaluation insight provided strategic insight to improve the operation of joint programmes. The SDG Fund adapts to the new context of development aid by placing a greater focus on sustainable development and public-private partnerships.
A cooperation mechanism for the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development
The SDG Fund incorporated several relevant changes:
- Greater participation of the private sector and improved public-private sector partnerships.
- A better selection of UN Agencies involved. Limiting the number of participating UN Agencies per programme to 4.
- Better mainstreaming of gender equality and women´s empowerment and integrating of environment sensitivity into future programmes. These 2 key areas are cross-cutting priorities that all programmes need to fulfill in their formulation.
- Engagement of local stakeholders. This is a key ingredient in designing and implementing programmes which target the most disadvantaged.
- Co-financing through national and international partners. Matching funds of national governments, international donors and the private sector will increase programme sustainability. See details of our financial information here.
- Multi-donor approach. The SDG-F is open to donors and partners that want to deploy joint programmes for the achievement of SDGs.
The SDG Fund works to turn development effectiveness principles into joint programmes that deliver results and advance sustainable development goals.

